3.8 Undecided Problems Team Teach
December 2023 (1411 Words, 8 Minutes)
What is an Undecidable Problem?
Some problems take a very long time to solve, so we use algorithms that give approximate solutions. There are some problems that a computer can never solve, even the world’s most powerful computer with infinite time: the undecidable problems.
- An decidable problem is a decision problem for which an algorithm can be written to produce a correct number for all inputs (eg: is the number even) (Collegeboard AAP-4.B.1)
- An undecidable problem is one for which no algorith can be constructed that is always capable of providing a correct yes-or-no answer. (Collegeboard AAP-4.B.2) An undecidable problem may have some instances that have an algorthimic solution, but there is no algorithmic solution that could solve all instances of the problem.
Popcorn Hack 1
1. Review of the Definition of an Undecided Problem
A company is developing a tool to detect “unreachable code”: code in a program that will never be executed because no paths ever lead to that line of code. They want to release the tool with the promise that it will “find and delete 100% of the unreachable code in your codebase!” Unfortunately, one of the programmers does some research and realizes that determining whether a line of code is unreachable is an undecidable problem.
What are the consequences of the problem being undecidable?
A. The programmers can come up with an algorithm that will find 100% of the unreachable code, but it would take an unreasonable amount of time to run.
B. The programmers can come up with an algorithm that correctly determines unreachable code most of the time, but it will not correctly identify unreachable code in all cases.
C. The programmers may be able to come up with an algorithm to find 100% of the unreachable code, but nobody has come up with the algorithm yet, so they will need more development time.
D. The tool will not be able to correctly identify any cases of unreachable code.
B because some algorithms are undecidable
Solution
B is the correct answer as the definition of an undecided problem states that an algorithm may be able to solve the problem in some cases but no algorithm exists to solve all cases.Halting Problem
The Halting Problem is a classic example of an undecidable problem in computer science, formulated by Alan Turing in the 1930s. It addresses the fundamental question of whether a program, given any input, will eventually halt (terminate) or run indefinitely (enter an infinite loop).
The essence of the Halting Problem revolves around creating an algorithm that can accurately determine, for any program and input, whether that program will halt or continue running forever. Alan Turing proved that such an algorithm cannot exist.
For example, consider this program that counts down:

That program will halt, since num eventually becomes 0. Compare that to this program that counts up:

It counts up forever, since num will never equal 0. Algorithms do exist that can correctly predict that the first program halts and the second program never does. These are simple programs which don’t change based on different inputs. However, no algorithm exists that can analyze any program’s code and determine whether it halts or not.
Popcorn Hack 2
2. Review of the Halting Problem
Which of the following options best summarizes the Halting Problem?
A. The Halting Problem is a decision problem in computability theory that seeks to determine whether a given algorithm will halt or run indefinitely for all possible inputs.
B. The Halting Problem is a sorting algorithm designed to arrange elements in ascending order.
C. The Halting Problem is a protocol used to secure communications over the internet.
D. The Halting Problem is a theorem in number theory that deals with prime numbers.
A because the halting problem has an issue with proof by contradiction
Solution
A is the correct answer as the Halting Problem was Turing's proof of the existence of an undecided problem.Turing’s Proof Through Contradiction:
defintion proof through contradiction: a form of proof that assumes a claim false and shows that this state leads to a known contradiction; therefore, the claim must be true
- We assume the halting algoritm exists So here’s the basic code flowchart for the halting algorithm:

Here’s the reverser (which consists of its halting algorithm) which basically does the opposite of the halting algoritm returns.
The Reverser works on programs such as Count Up or Count Down until 0.
- The contradiction But if we plug Reverser into itself….
Reverser does the opposite of HaltChecker so HaltChecker can never be right.

- Yellow path: If HaltChecker says that Reverser never halts; the Reverser will halt
- Green Path: If HaltCheck says Reverser halts; the Reverser will never halt
However, we said that HaltChecker exists and is always correct.
- Conclusion Therefore, HaltChecker cannot exist.
Implications and Other Undecidable Problems
- Consequences:
- Because proof of the Halting Problem is undecidable, this has implications in the field of computer science. There are consequences for the theory of computation, algorithmic complexity, and the limits of what can be achieved with computers.
- The Post Correspondence Problem (PCP)
- Definition:
- A mathematical problem that involves a set of rectangular tiles, each marked with a string of symbols on the top and bottom. The challenge is to determine whether a sequence of these tiles exists such that when they are arranged in a line (either horizontally or vertically), the strings on the top and bottom of the tiles match.

- Undecidability:
- Alan Turing demonstrated that no algorithm can determine this sequence for all sets of tiles from the Turing machine not accepting the post correspondence input.
- Because it is simpler than the halting problem and the Entscheidungsproblem it is often used in proofs of undecidability.
- Alan Turing demonstrated that no algorithm can determine this sequence for all sets of tiles from the Turing machine not accepting the post correspondence input.
- Definition:
- Rice’s Theorem
- Definition:
- Any non-trivial property about the behavior of a computer program is undecidable.
- “non-trivial property” means a property that is true for some programs and false for others
- Any non-trivial property about the behavior of a computer program is undecidable.
- Undecidability: If you have a question about what a program does that is interesting, there is no algorithm that can always give you the correct answer.
- Definition:
- The Collatz Conjecture
- Definition:
- is a mathematical hypothesis that posits that, no matter what positive integer you start with, the rule states that if the current number is even, divide it by 2; if it’s odd, multiply it by 3 and add 1. Despite its apparent simplicity, proving or disproving the conjecture remains an unsolved problem in mathematics.

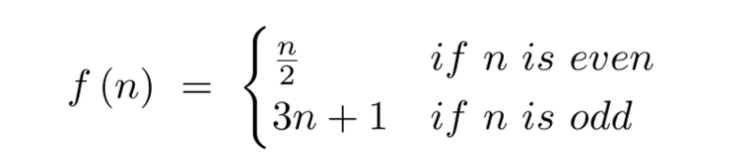
- Undecidability:
- Sequence will always end up reaches 4-2-1 from any starting number and will loop infintely since 1 is odd leading back to 4.
- Definition:
- The Tiling Problem
- Definition:
- Determines if a given shape can be tiled perfectly without gaps or overlaps. The objective is to find a way to arrange the tiles to fill the entire area of the given shape. The challenge is to determine if a valid tiling arrangement exists and, if so, to find one or more solutions.

- Undecidability: Proving whether an arbitrary shape can be tiled without gaps or overlaps is undecidable.
- Definition:
- The Entscheidungsproblem
- Definition:
- The Entscheidungsproblem, or Decision Problem in English, was a question in the field of mathematical logic posed by David Hilbert in 1928. It asked whether there exists a general algorithm to determine the truth or falsity of any mathematical statement. This question led to important developments in the study of computability and laid the groundwork for the field of theoretical computer science.
- Undecidability:
- In 1936 and 1937, Alonzo Church and Alan Turing showed independently, that there can be no answer to the Entscheidungsproblem. They showed that it is impossible for an algorithm to decide whether statements in arithmetic are true or false. For this reason, there can be no solution for the Entscheidungsproblem. This was proven by Alan Turing’s “Turing Machine” which was created in the 1930s.
- Definition:
Popcorn Hack 3
3. Review of Alternative Examples of Undecided Problems
Which of the following options is not an example of an undecidable problem?
A. Halting Problem
B. The Collatz Conjecture
C. Rice’s Theorem
D. Bubble sorting
D because it was not mentioned
Solution
D is the correct answer as the other three options are part of the previously discussed examples of undecided problems.Homework
Please review and read the lesson and then answer the google form questions.
Summary:
- Undecidable problems are computing problems which can never be solved even given an infinite amount of time and computing power
- Proof through contradiction: a form of proof that assumes a claim false and shows that this state leads to a known contradiction; therefore, the claim must be true